- Comma-separated files (.csv) or tab-separated files (.txt), seehow to import data from a structured text file,
- Files with fixed-width columns without delimiters between data columns where data starts at fixed positions of the line:
- Microsoft Excel 2016 Text Import Wizard
- Text Import Wizard Excel 2016 Download
- Excel Text Import Wizard Settings
The Text Import Wizard offers a lot of options to customize this type of import. You can specify how you’d your text data to be imported, minimizing the amount of cleanup that you need to do on the data. In this section, we’ll use IdealGasPropertyData.txt as the data source. Go to Data Get External Data From Text, and open that file. How to Import a Text file into Excel - Office 365. This video explains how to import data from a text file in to excel. Using Excel2016 (with Legacy Import hidden) importing fixed-width text files (without delimiters) is no longer working as well as it used to. Turning on the legacy import option allows the easy import of these files; however, I was able to use the new data import transform editor thing (you know what I mean!) to make the import work OK, and be. I'm trying to import a space delimited Word doc into Excel, but Excel is not recognizing the ' symbol as a text qualifier. For example, 'Dallas TX' is importing into two columns instead of one. I've tried using a Mac vs. Windows and saving the document with different encoding options, but nothing seems to work. Importing CSV via Data From Text is - altough working - rather cumbersome: You need to select the file, the wizard asks about 'Delimited' or 'Fixed width', then you need to select 'Comma' as seperator and finally how to import the data. And when you want to reimport later on the whole procedure starts again and again and again.
To import data from a text file, do the following:
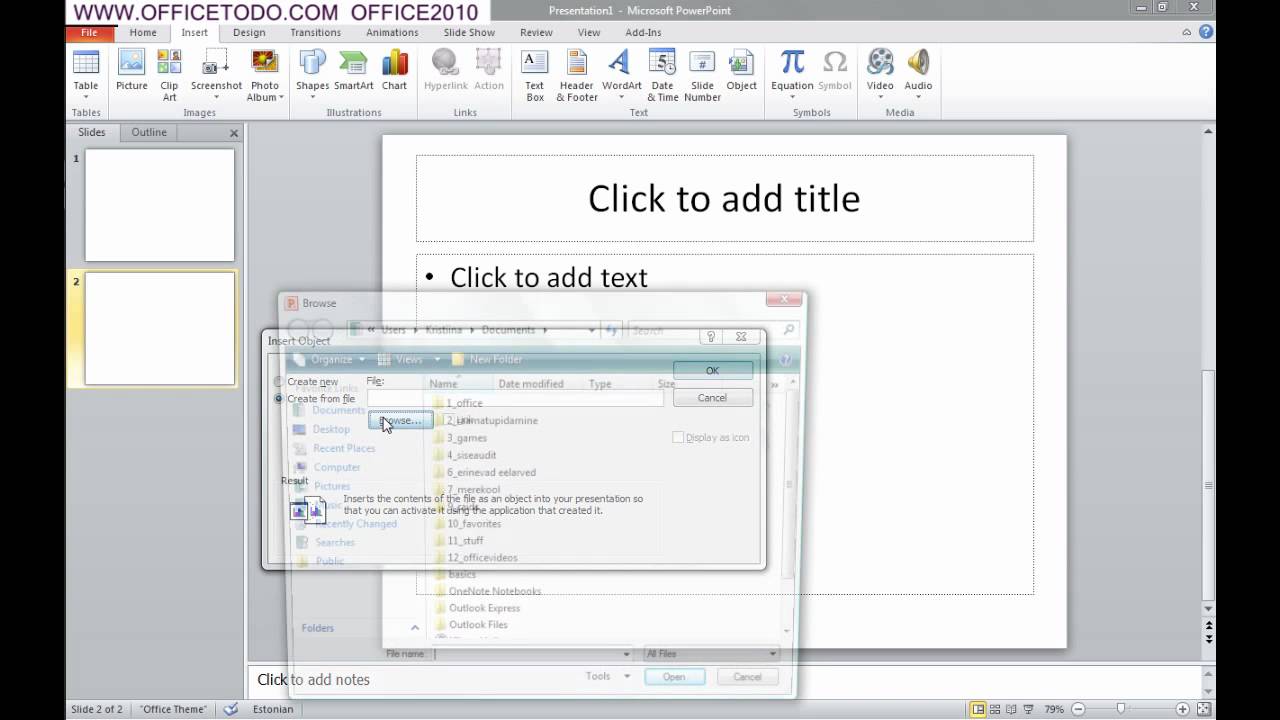
1. On the File tab, click Open (or clickCtrl+O).
2. On the Open pane, click the Browse button:
3. On the Open dialog box:
- Select the path to the text file you want to import,
- From the File Type dropdown list, select All Files or Text Files:
- Click the Open button.
4. In the Text Import Wizard – Step 1 of 3 dialog box:
4.1. In the Original data type group, choose the Fixed width option:
Note: If you see delimiters, leave the option Delimited selected and follow the steps ofimporting a structured text file.
4.2. You can change the File origin to use another encoding todisplay the data (you need to know the character encoding for the data or try other encodings until yousee the correct data in the preview section):
4.3. Click the Next > button.
5. In the Text Import Wizard – Step 2 of 3 dialog box:
5.1. Create, move, and delete break lines:
5.2. Click the Next > button.
6. In the Text Import Wizard – Step 3 of 3 dialog box:
6.1. Select the column and the appropriate data format for this column in the Column data format group:
Notes:
- You can skip this step and format columns after importing.
- You can click the Advanced... button to select the correct Decimal separator andThousands separator (seehow to change used by default decimal symbol and digit grouping symbol):
- You can ignore some columns for importing by selecting the Do not import column (skip) in theColumn data format group (the second column Session in the previous example).
6.2. Repeat the previous step for all columns you want to import andclick Finish.
Excel imports all the data you selected:
-->Applies to:
There are several ways to import data from Excel files to SQL Server or to Azure SQL Database. Some methods let you import data in a single step directly from Excel files; other methods require you to export your Excel data as text (CSV file) before you can import it. This article summarizes the frequently used methods and provides links for more detailed information.
List of methods
You can use the following tools to import data from Excel:
| Export to text first (SQL Server and SQL Database) | Directly from Excel (SQL Server on-premises only) |
|---|---|
| Import Flat File Wizard | SQL Server Import and Export Wizard |
| BULK INSERT statement | SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) |
| BCP | OPENROWSET function |
| Copy Wizard (Azure Data Factory) | |
| Azure Data Factory |
If you want to import multiple worksheets from an Excel workbook, you typically have to run any of these tools once for each sheet.
A complete description of complex tools and services like SSIS or Azure Data Factory is beyond the scope of this list. To learn more about the solution that interests you, follow the provided links.
Important
For detailed info about connecting to Excel files, and about limitations and known issues for loading data from or to Excel files, see Load data from or to Excel with SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS).
If you don't have SQL Server installed, or you have SQL Server but don't have SQL Server Management Studio installed, see Download SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
SQL Server Import and Export Wizard
Import data directly from Excel files by stepping through the pages of the SQL Server Import and Export Wizard. Optionally, save the settings as a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package that you can customize and reuse later.
In SQL Server Management Studio, connect to an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine.
Expand Databases.
Right-click a database.
Point to Tasks.
Click one of the following options.
Import Data
Export Data
For an example of using the wizard to import from Excel to SQL Server, see Get started with this simple example of the Import and Export Wizard.
To learn about other ways to launch the Import and Export wizard, see Start the SQL Server Import and Export Wizard.
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
If you're familiar with SSIS and don't want to run the SQL Server Import and Export Wizard, create an SSIS package that uses the Excel Source and the SQL Server Destination in the data flow.
For more info about these SSIS components, see the following topics:
To start learning how to build SSIS packages, see the tutorial How to Create an ETL Package.
OPENROWSET and linked servers
Important
In Azure SQL Database, you cannot import directly from Excel. You must first export the data to a text (CSV) file. For examples, see Example.
Note
The ACE provider (formerly the Jet provider) that connects to Excel data sources is intended for interactive client-side use. If you use the ACE provider on SQL Server, especially in automated processes or processes running in parallel, you may see unexpected results.
Distributed queries
Import data directly into SQL Server from Excel files by using the Transact-SQL OPENROWSET or OPENDATASOURCE function. This usage is called a distributed query.
Important
In Azure SQL Database, you cannot import directly from Excel. You must first export the data to a test (CSV) file. For examples, see Example.
Before you can run a distributed query, you have to enable the ad hoc distributed queries server configuration option, as shown in the following example. For more info, see ad hoc distributed queries Server Configuration Option.
The following code sample uses OPENROWSET to import the data from the Excel Sheet1 worksheet into a new database table.
Here's the same example with OPENDATASOURCE.
To append the imported data to an existing table instead of creating a new table, use the INSERT INTO ... SELECT ... FROM ... syntax instead of the SELECT ... INTO ... FROM ... syntax used in the preceding examples.
To query the Excel data without importing it, just use the standard SELECT ... FROM ... syntax.
For more info about distributed queries, see the following topics:
- Distributed Queries (Distributed queries are still supported in SQL Server 2016, but the documentation for this feature has not been updated.)
Linked servers
You can also configure a persistent connection from SQL Server to the Excel file as a linked server. The following example imports the data from the Data worksheet on the existing Excel linked server EXCELLINK into a new SQL Server database table named Data_ls.
You can create a linked server from SQL Server Management Studio, or by running the system stored procedure sp_addlinkedserver, as shown in the following example.
For more info about linked servers, see the following topics:
For more examples and info about both linked servers and distributed queries, see the following topics:
Prerequisite - Save Excel data as text
To use the rest of the methods described on this page - the BULK INSERT statement, the BCP tool, or Azure Data Factory - first you have to export your Excel data to a text file.
In Excel, select File | Save As and then select Text (Tab-delimited) (*.txt) or CSV (Comma-delimited) (*.csv) as the destination file type.
If you want to export multiple worksheets from the workbook, select each sheet and then repeat this procedure. The Save as command exports only the active sheet.
Tip
For best results with data importing tools, save sheets that contain only the column headers and the rows of data. If the saved data contains page titles, blank lines, notes, and so forth, you may see unexpected results later when you import the data.
The Import Flat File Wizard
Import data saved as text files by stepping through the pages of the Import Flat File Wizard.
As described previously in the Prerequisite section, you have to export your Excel data as text before you can use the Import Flat File Wizard to import it.
For more info about the Import Flat File Wizard, see Import Flat File to SQL Wizard.
BULK INSERT command
BULK INSERT is a Transact-SQL command that you can run from SQL Server Management Studio. The following example loads the data from the Data.csv comma-delimited file into an existing database table.
As described previously in the Prerequisite section, you have to export your Excel data as text before you can use BULK INSERT to import it. BULK INSERT can't read Excel files directly. With the BULK INSERT command, you can import a CSV file that is stored locally or in Azure Blob storage.
For more info and examples for SQL Server and SQL Database, see the following topics:
BCP tool
BCP is a program that you run from the command prompt. The following example loads the data from the Data.csv comma-delimited file into the existing Data_bcp database table.
As described previously in the Prerequisite section, you have to export your Excel data as text before you can use BCP to import it. BCP can't read Excel files directly. Use to import into SQL Server or SQL Database from a test (CSV) file saved to local storage.
Important
For a text (CSV) file stored in Azure Blob storage, use BULK INSERT or OPENROWSET. For an examples, see Example.
For more info about BCP, see the following topics:
Copy Wizard (Azure Data Factory)
Import data saved as text files by stepping through the pages of the Azure Data Factory Copy Wizard.
As described previously in the Prerequisite section, you have to export your Excel data as text before you can use Azure Data Factory to import it. Data Factory can't read Excel files directly.
For more info about the Copy Wizard, see the following topics:
- Tutorial: Create a pipeline with Copy Activity using Data Factory Copy Wizard.
Azure Data Factory
Microsoft Excel 2016 Text Import Wizard
If you're familiar with Azure Data Factory and don't want to run the Copy Wizard, create a pipeline with a Copy activity that copies from the text file to SQL Server or to Azure SQL Database.
As described previously in the Prerequisite section, you have to export your Excel data as text before you can use Azure Data Factory to import it. Data Factory can't read Excel files directly.
For more info about using these Data Factory sources and sinks, see the following topics:
To start learning how to copy data with Azure data factory, see the following topics:
Common errors
Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' has not been registered
This error occurs because the OLEDB provider is not installed. Install it from Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable. Be sure to install the 64-bit version if Windows and SQL Server are both 64-bit.
The full error is:
Cannot create an instance of OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' for linked server '(null)'
This indicates that the Microsoft OLEDB has not been configured properly. Run the following Transact-SQL code to resolve this:
The full error is:
The 32-bit OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' cannot be loaded in-process on a 64-bit SQL Server
This occurs when a 32-bit version of the OLD DB provider is installed with a 64-bit SQL Server. To resolve this issue, uninstall the 32-bit version and install the 64-bit version of the OLE DB provider instead.
The full error is:
Text Import Wizard Excel 2016 Download
The OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' for linked server '(null)' reported an error. The provider did not give any information about the error

Cannot initialize the data source object of OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' for linked server '(null)'
Both of these errors typically indicate a permissions issue between the SQL Server process and the file. Ensure that the account that is running the SQL Server service has full access permission to the file. We recommend against trying to import files from the desktop.
The full errors are: